Blood Components and Functions
Blood is a liquid connective tissue, which is maintained in constant circulation round the body. In certain organisms, blood flows within a closed system of inter connecting vessels while the reverse holds in other organisms.
The human blood is of PH 7.4 and comprises four components:
- Plasma [liquid part of blood]
- Red Blood cells [Erythrocytes]
- White Blood Cells [Leucocytes]
- Blood platelets [Thrombocytes]
PLASMA
This is the liquid part of blood, which makes up about 55% volume of blood. The plasma itself is made of about 90% water, proteins and mineral salts. It takes digested food from the small intestine to places where needed and also takes waste product to the excretory organs for removal.
RED BLOOD CELLS: These are the most numerous cells in the blood. They account for the redness of blood. Each red cell contains HEAMOLOGIN, a respiratory pigment which enables Red Blood Cells to transport oxygen in the blood. Red blood cells are also called ERYTHROCYTES. They are formed in the BONE MARROW and destroyed in the LIVER and SPLEEN when too old to perform their functions completely after about 120days of existence.
WHITE BLOOD CELLS
They are the least numerous cells in the blood. They fight microorganisms and infections in the blood. WBC also helps the body to destroy bacteria and viruses through the agency of ANTIBODIES in the blood plasma.
PLATELETS
The second most numerous blood cells which help blood to clot in wounds. They are also called THROMBOCYTES. They are tiny cells, which are much smaller than either the RBCs or WBCs. Most often they are found as fragments.
The Heart and Blood vessels
The heart is the muscular pumping organ, which maintains a continual flow of blood round the body. The human heart comprises four chambers namely:
- The 2 upper and smaller chambers [ARTRIA or AURICLES]
- The 2 Lower and bigger chambers called VENTRICLES
The heart is connected to blood vessels within which blood is transported round the body.
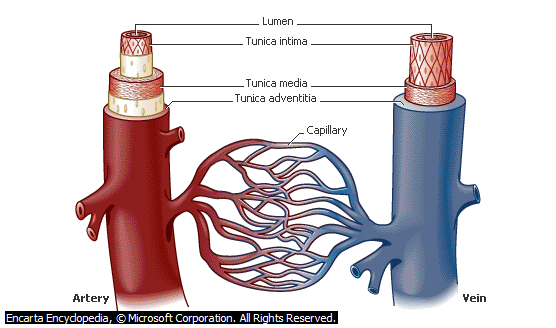
THE BLOOD VESSELS
Three types of blood vessels known are:
Veins : Return blood to the heart
Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart.
Capillaries: Link arteries with venules
Differences between Arteries and Vein
ARTERIES VEINS
- Carry blood away from the heart Returns blood to the heart
- Carry oxygenated blood at high Carry deoxygenated blood under low pressure pressure
3. Are deeply located under the skin. Are superficially located
See also